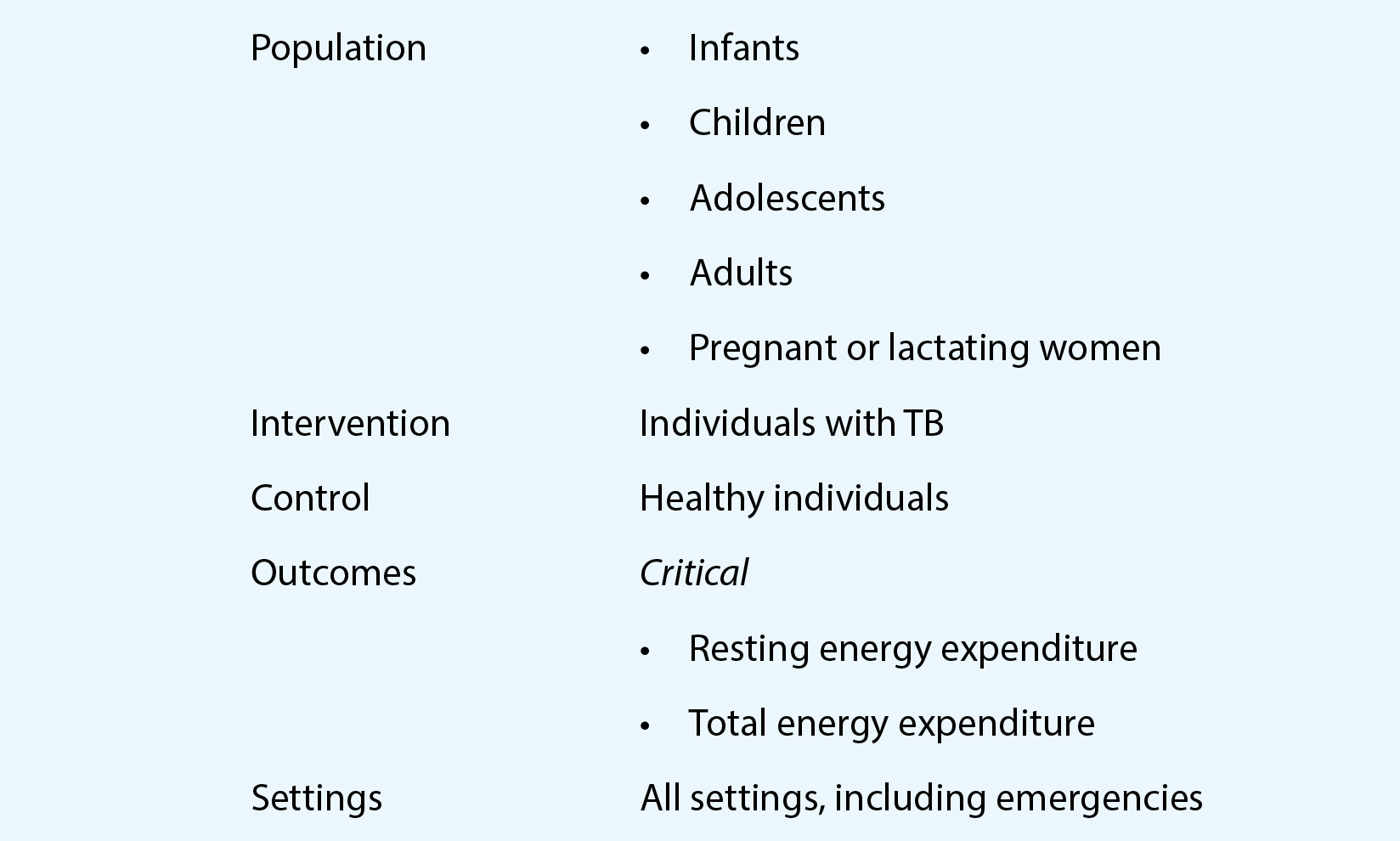
1. Scope and purpose
The aim of this guideline is to help improve health outcomes for people with tuberculosis (TB), through improved nutritional care and support. The objectives of the guideline are to provide guidance on nutritional assessment, advice and treatment, for integration into clinical care for people with TB. Five guiding principles for nutritional care and support for people with TB are presented. The focus is on nutrition assessment, counselling and management to improve the clinical care of people with TB.

 Feedback
Feedback