Operational Handbooks
Executive summary
The WHO operational handbook on tuberculosis, Module 4: treatment and care provides practical guidance on implementing recommendations to achieve national and global impact in tuberculosis (TB) management. It consolidates three key components of the WHO consolidated guidelines on tuberculosis treatment: drug-susceptible TB (DS-TB) treatment, drug-resistant TB (DR-TB) treatment, and tuberculosis care and support. This consolidated operational handbook complements the WHO consolidated guidelines on TB treatment, assisting Member States, technical partners and other stakeholders who
Abbreviations and acronyms
aDSM
active tuberculosis drug-safety monitoring and management
AE
adverse event
AIDS
acquired immunodeficiency syndrome
ALT
alanine aminotransferase
Definitions
Adverse event: Any untoward medical occurrence that may present in a person with tuberculosis (TB) during treatment with a pharmaceutical product but that does not necessarily have a causal relationship with the treatment.
Bacteriologically confirmed TB case: A case from whom a biological specimen is positive by smear microscopy, culture or a World Health Organization (WHO) recommended rapid diagnostic (e.g. Xpert® MTB/RIF).
Acknowledgements
Consolidation of the operational handbook (2025)
Consolidation of the operational handbook was carried out by Medea Gegia, Fuad Mirzayev, and Linh Nguyen under the overall direction of Matteo Zignol and Tereza Kasaeva.
Annex 6. A standardized checklist for periodic evaluation of TB infection prevention and control
This checklist is based on one produced by Médecins Sans Frontières (1).
Instructions: This tool provides an idea of the risk of transmission of M. tuberculosis in a health-care facility or congregate setting. The results should be completed by the IPC focal person and interpreted by the IPC committee. For the Yes/No questions, a Yes answer indicates good TB IPC practices. Any pertinent information on No answers is noted in the Comments section below each table.
Annex 5. Examples of recording and reporting forms
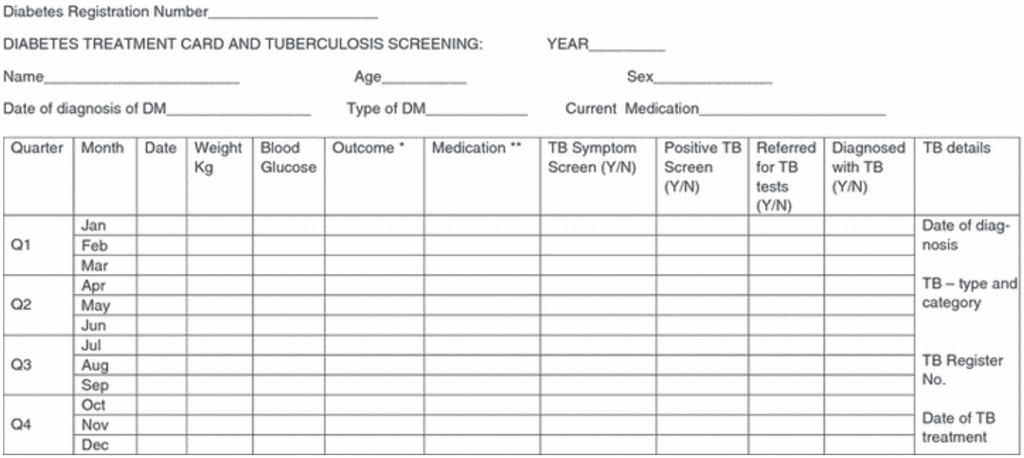
TB epidemiological surveillance form
Annex 4. Monitoring and evaluation of collaborative TB/DM activities
Continued monitoring of collaborative TB/DM activities and evaluation of their impact is critical for scaling up, for monitoring progress and for identifying gaps in implementation. This requires an effective, efficient monitoring and evaluation system. Table A.4.1. summarizes suggested core indicators for monitoring and evaluating collaborative TB/DM activities.
Table A.4.1. Summary of indicators for monitoring and evaluating collaborative TB/DM activities
Pagination
- Previous page
- Page 10
- Next page

 Feedback
Feedback
