4. Treatment of rifampicin-susceptible and isoniazid-resistant TB (Hr-TB)
Recommendations 4.1–4.2 Treatment of Hr-TB

Justification and evidence
The recommendations in this section address one PICO question:
 TB KaSPar
TB KaSPar
 Feedback
Feedback
Recommendations 4.1–4.2 Treatment of Hr-TB

Justification and evidence
The recommendations in this section address one PICO question:
Recommendations 3.1–3.17 Longer regimens
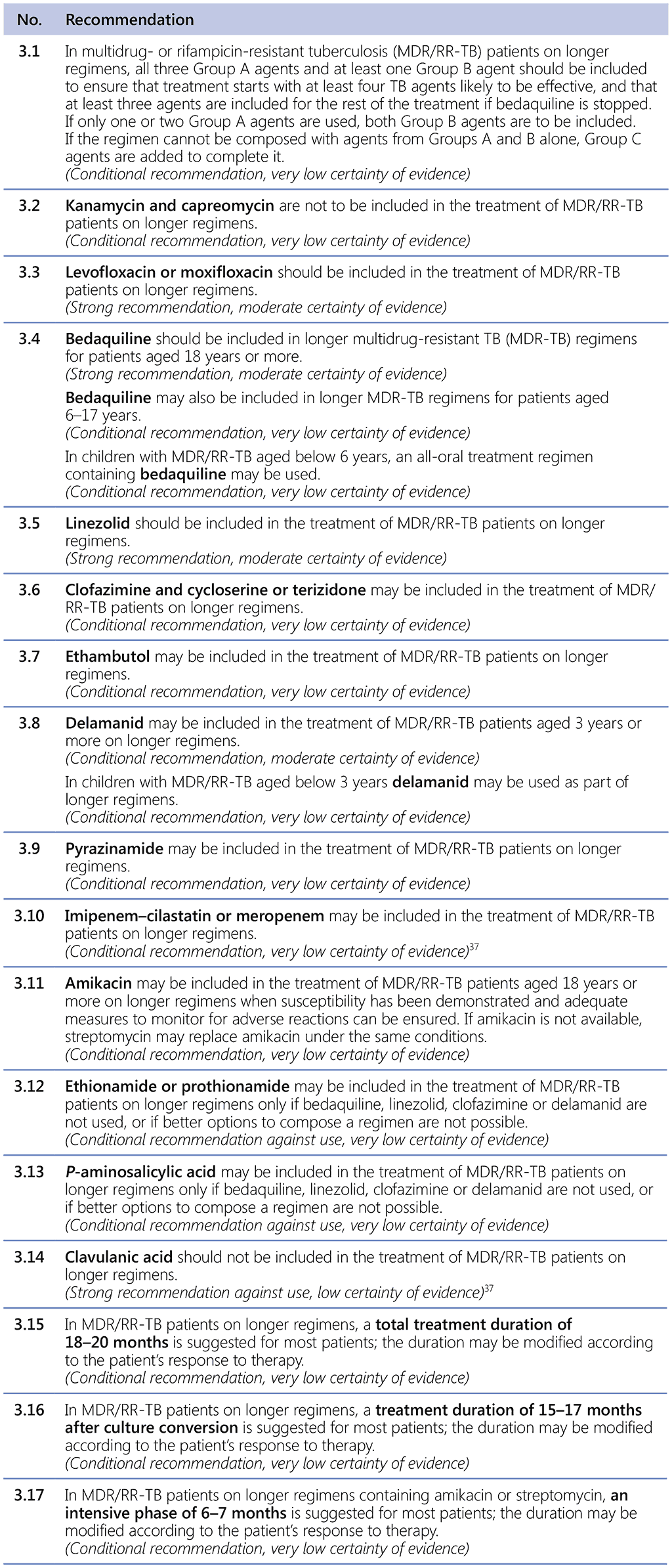
Table 3.1 gives details of the grouping of medicines recommended for use in longer MDR-TB regimens; the groups are summarized here for clarity:

Remarks

Remarks
These guidelines are primarily targeted at policy-makers in ministries of health, or managers of NTPs who formulate country-specific TB treatment guidelines or are involved in the planning of TB treatment programmes. It is expected that these updated recommendations will also be used by health professionals, including doctors, nurses and educators working in governmental and nongovernmental organizations, and by technical agencies involved in treating patients and organizing treatment services.
The recommendations for the treatment of DR-TB that are presented in this document have been derived from earlier WHO guideline documents (Box 1), and a WHO guideline development conducted in June 2024. These recommendations supersede the WHO consolidated guidelines on tuberculosis. Module 4: Treatment – drug-resistant tuberculosis treatment, that were published in 2022 (3).
This chapter provides specific recommendations on the treatment of DR-TB, including the use of regimens for rifampicin-susceptible, isoniazid-resistant TB (Hr-TB), shorter and longer regimens for MDR/RR-TB, monitoring patient response to MDR/RR-TB treatment, starting ART in patients on secondline anti-TB regimens, undertaking surgery for patients on DR-TB treatment and co-administration of MDR/RR-TB and HCV therapies.
The 2024 GDG meeting convened by WHO resulted in two new recommendations: the use of a new 6-month regimen and modified 9-month regimens.
Effective treatment of TB, including its drug-resistant forms, relies on the use of several medicines administered in combination for an adequate duration. Significant progress has been made in recent years in identifying more efficacious, safer medicines and shorter treatment regimens. Since the 1990s, WHO has regularly evaluated evidence on the use of specific drug compositions and combinations of regimens of different durations (2, 9–16). Historically, patients with certain drugresistance patterns were often treated for 20 months or longer.
The recommendations part of this chapter has eight sections that cover aspects of the treatment of DR-TB. The aspects covered are: