5.2.10.4. Overview of common adverse events and their management
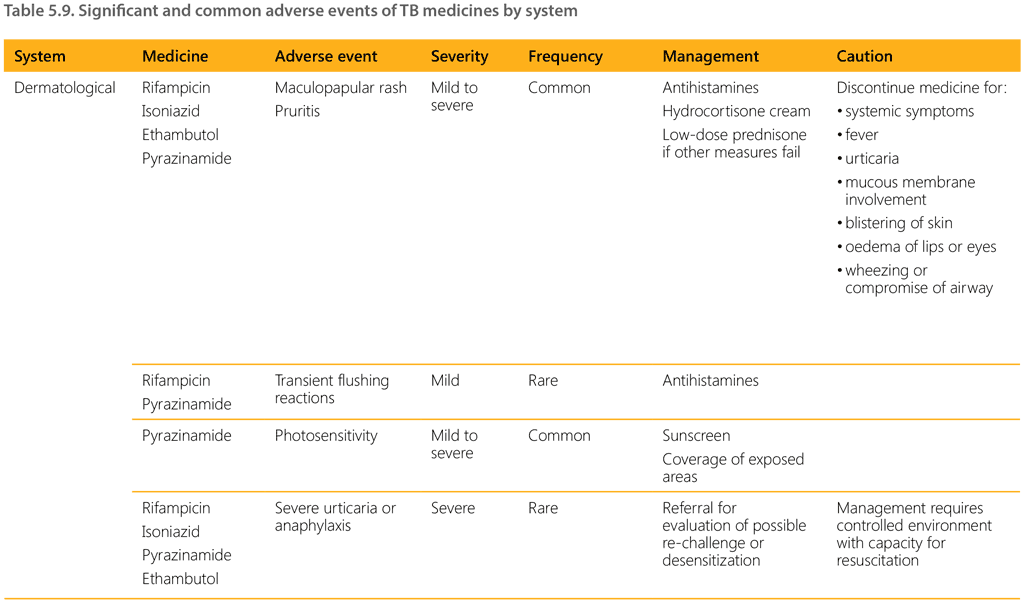
Table 5.9 gives an overview of common adverse events and their management.
 TB KaSPar
TB KaSPar
 Feedback
Feedback
Table 5.9 gives an overview of common adverse events and their management.

Malnutrition results in the reduction of cell-mediated immunity, thereby increasing the risk of diseases such as TB. The catabolic effect of TB disease results in weight loss and wasting, which in turn worsens the malnutrition, creating a vicious cycle (104).
Corticosteroids should be used as part of the treatment for TBM and may be used for the treatment of tuberculous pericarditis. Corticosteroids are sometimes used for other complicated forms of TB (e.g. complications of airway obstruction by TB lymph nodes; severely ill children and adolescents with disseminated TB), but there are no WHO recommendations regarding use of corticosteroids for forms of EPTB disease other than TBM and tuberculous pericarditis (102).
All children and adolescents with severe forms of TB (TBM, peritonitis, pericarditis, renal, spinal, disseminated or osteoarticular TB) and those suspected of having MDR/RR-TB (in contact with a person with confirmed or suspected MDR/RR-TB, or children and adolescents diagnosed with TB who are not responding to first-line TB treatment) should be referred to a specialist for further management if management capacity where they present is insufficient.
Following infection with M. tuberculosis, young children are at high risk of developing the most severe forms of disease, of which the most devastating is TBM. This mainly affects young children (4). Up to 15% of childhood TB presents as TBM (92). With a decreasing incidence of bacterial meningitis attributed to other causes, TB is the leading cause of bacterial meningitis in many settings (93). TBM is associated with significant mortality and morbidity.
Children aged between 3 months and 16 years with EPTB limited to peripheral lymph nodes (i.e. without involvement of other sites of disease) should be treated with the shorter regimen (2HRZ(E)/2HR). Children with forms of drug-susceptible EPTB other than TBM and osteoarticular TB should be treated with a 6-month treatment regimen of 2HRZE/4HR. Children with osteoarticular TB should be treated with 2HRZE/10HR.
Given the increased risk of treatment failure and drug resistance, children and adolescents who had been treated in the preceding 2 years were not eligible for inclusion in the SHINE trial. These children should be treated with the 6-month treatment regimen (2HRZ(E)/4HR).
Children and young adolescents with PTB who do not meet the eligibility criteria for the 4-month regimen should be treated with a standard 6-month regimen that includes a fourth drug – ethambutol – in the intensive phase (2HRZE/4HR).
Children presenting with severe acute pneumonia who are diagnosed with TB should be treated for 6 months (2HRZE/4HR) in view of the severity of their symptoms, which, according to the definition of severe acute pneumonia, include cough or difficulty in breathing with at least one of the following:
No separate subgroup analysis could be conducted for children with SAM (defined as weight-forheight Z-score below −3 or mid-upper arm circumference below 115 mm (91)) in the SHINE trial due to the low numbers (30 children with SAM in the 16-week arm and 33 in the 24-week arm). As SAM is defined as a danger sign, even if children with SAM have a non-severe form of TB they should preferably receive 6 months of TB treatment.