Consolidated Guidelines
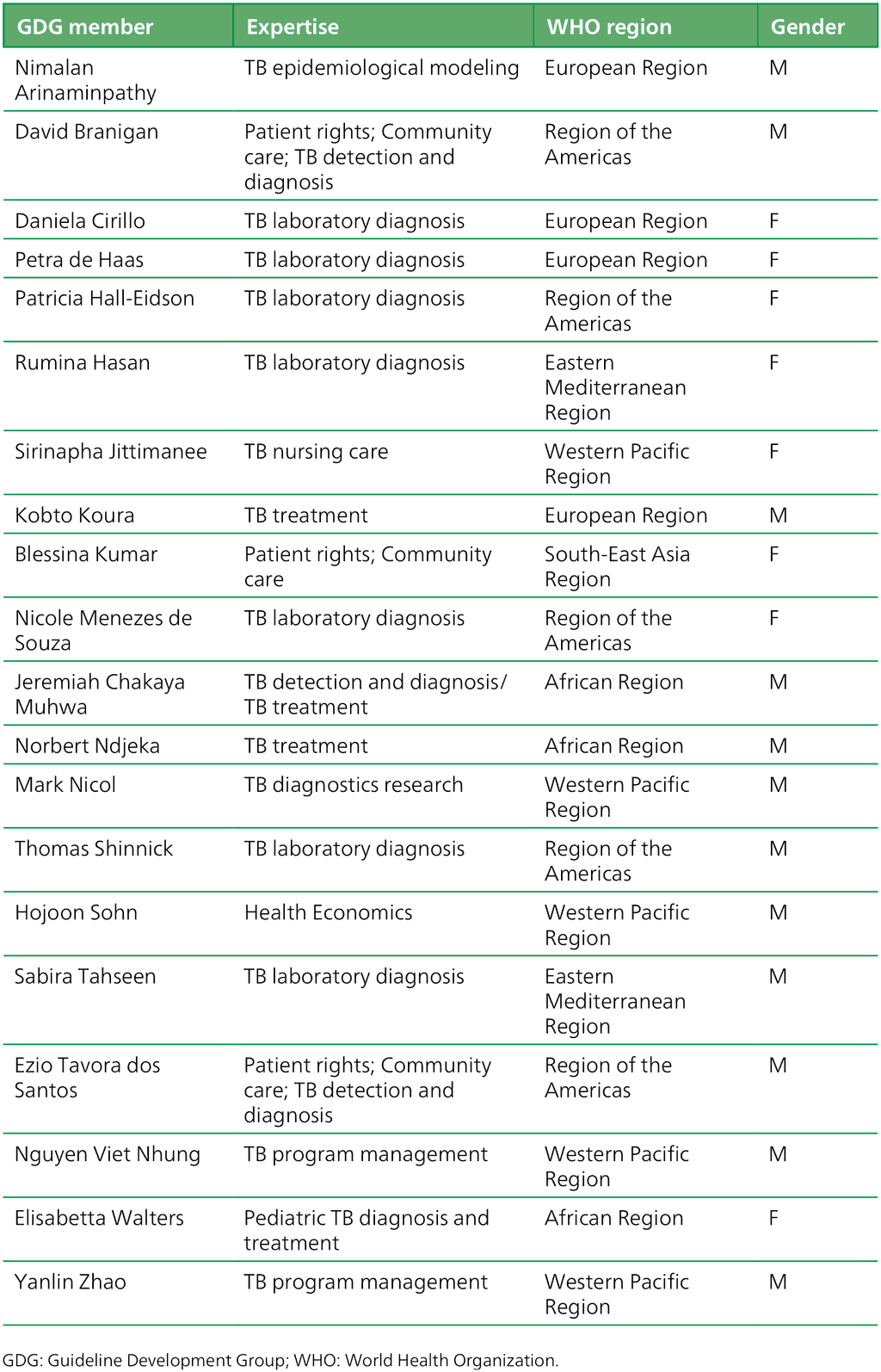
Annex 3. GDG members expertise, region, gender
Table A.3.1. Guideline development group members: “Targeted next-generation sequencing” 2–5 May 2023
Annex 2. Conflict of interest assessment for Guideline Development Group and External Review Group members
Before being considered for group membership, each Guideline Development Group (GDG) and External Review Group candidate was required to submit a completed declaration of interest (DOI) form. In addition, a preliminary internet search was performed to identify any obvious public controversies or interests that may lead to compromising situations for the World Health Organization (WHO) and the expert concerned.
3.4. References
- Public announcement to TB in vitro diagnostics manufacturers, procurement agencies and national TB programmes on inclusion of WHO prequalification for TB in vitro diagnostics. Geneva: World Health Organization; 2021 (https://extranet.who.int/pqweb/sites/default/files/documents/210211_PublicAnnouncement_TB_%20in-vitro-diagnostics.pdf).
- Schünemann HJ, Mustafa RA, Brozek J, Steingart KR, Leeflang M, Murad MH et al. GRADE guidelines: 21 part 2.
Annex 1. Guideline development methods
Methods used to develop World Health Organization guidelines
To develop new or update existing guidelines for methods and tools to diagnose tuberculosis (TB), the World Health Organization (WHO) Global TB Programme commissions systematic reviews on the performance or use of the tool or method in question. A systematic review provides a summary of the current literature on diagnostic accuracy or user aspects, for the diagnosis of TB or the detection of anti-TB drug resistance in adults or children (or both) with signs and symptoms of TB.
3.2. TB skin tests and interferon gamma release assays for the diagnosis of TB infection
Testing for TB infection increases the certainty that individuals targeted for treatment will benefit from it. However, there is no gold-standard test to diagnose TB infection. Both currently available tests – the TST and IGRAs – are indirect and require a competent immune response to identify people infected with TB. A positive test result by either method is not by itself a reliable indicator of the risk of progression to active disease. This section discusses the evidence and the recommendations for TB infection testing.
3.1. Mycobacterium tuberculosis antigen-based skin tests for the diagnosis of TB infection
Since 2011, the World Health Organization (WHO) has issued recommendations on the use of IGRAs for the diagnosis of TB infection. In 2018, WHO updated the recommendations to stipulate that the TST or IGRAs (or both) can be used to test for TB infection in LMIC. The TST is a widely used point-of-care test that involves intradermal injection of purified protein derivative (PPD), a crude mixture of different mycobacterial antigens, which stimulates a delayed-type hypersensitivity response and causes induration at the injection site within 48–72 hours.
2.5. References
- Global tuberculosis report 2024. Geneva: World Health Organization; 2024 (https://www.who.int/teams/global-tuberculosis-programme/tb-reports/global-tuberculosis-report-2024).
- Resolution 78/L.4. Political declaration of the high-level meeting of the General Assembly on the fight against tuberculosis.
Pagination
- Previous page
- Page 3
- Next page

 Feedback
Feedback