Перекрёстные ссылки книги для ПЛАТФОРМА ВОЗ ПО ОБМЕНУ ЗНАНИЯМИ О ТБ
A4.1. Dosages of anti-TB medicines by weight band for treatment of DS-TB
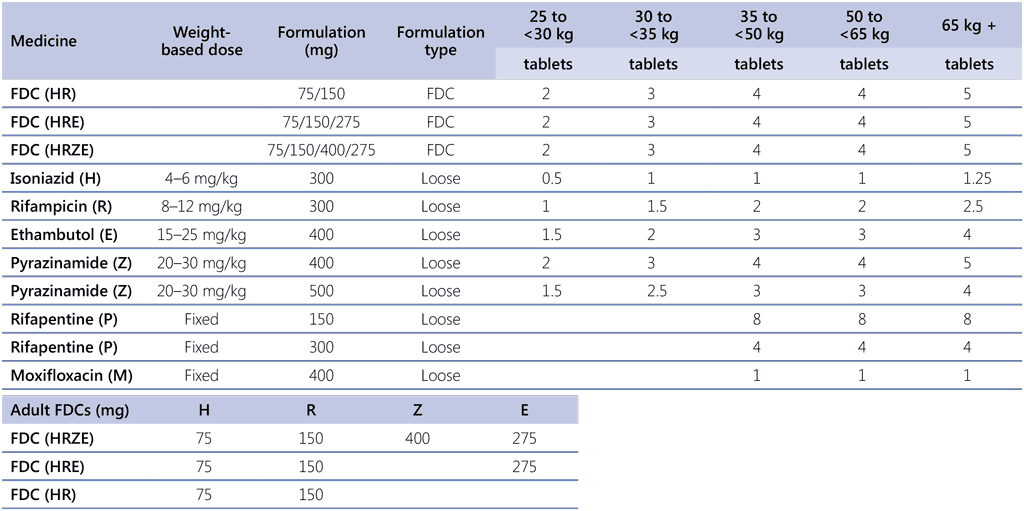
DS-TB: drug-susceptible TB; FDC: fixed-dose combination; TB: tuberculosis
A4.2. Weight-based dosing of medicines used in multidrug-resistant TB regimens, adults and childrenᵃ
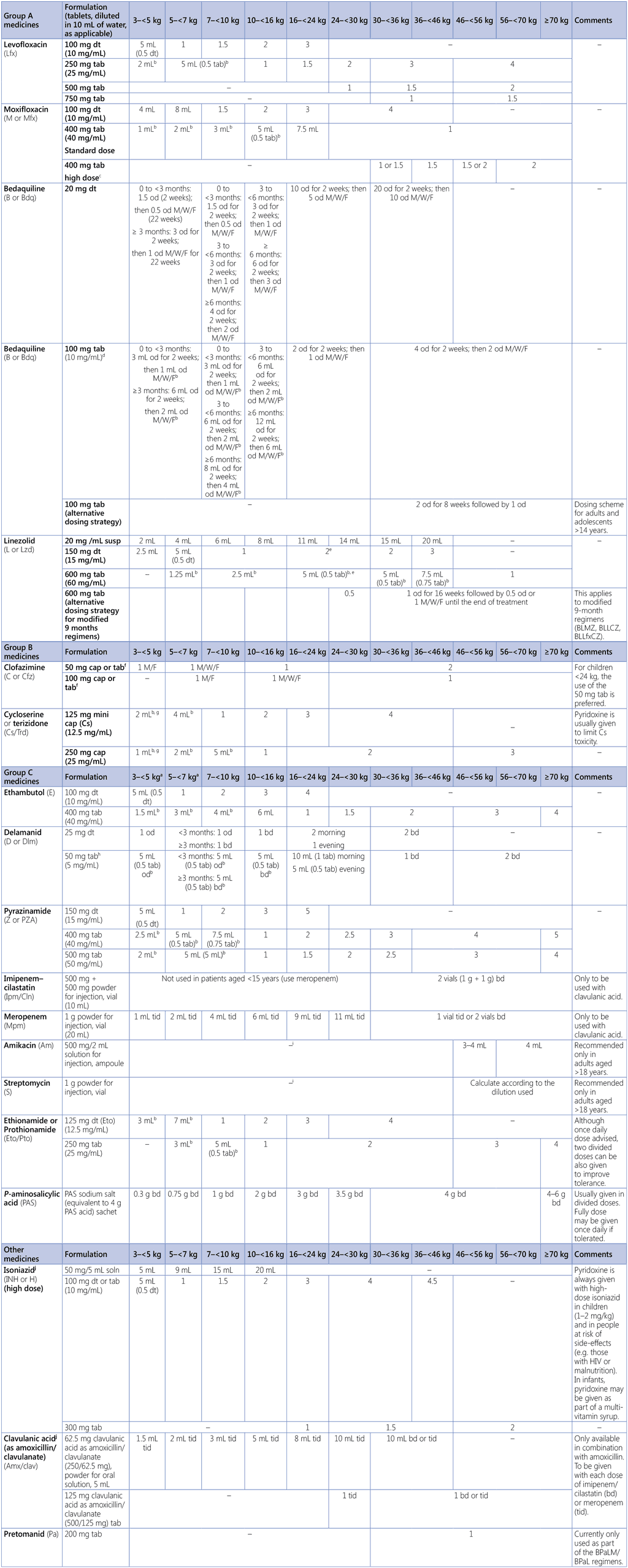
bd: two times a day; BPaL: bedaquiline, pretomanid and linezolid; BPaLM: bedaquiline, pretomanid, linezolid and moxifloxacin; cap: capsule; DR-TB: drug-resistant TB; dt: dispersible tablet; g: gram; GDG: Guideline Development Group; HIV: human immunodeficiency virus; kg: kilogram; MDR-TB: multidrug-resistant TB; MDR/RR-TB: multidrug- or rifampicin-resistant TB; mg: milligram; mL: millilitre; M/F: Monday and Friday; M/W/F: Monday, Wednesday and Friday; od: once daily; soln: solution; susp: suspension; tab: tablet; TB: tuberculosis; tid: three times a day; WHO: World Health Organization.
a Dosing guidance is based on currently available data and may be revised once additional data are available. Dosages were established by the GDGs for the WHO guidelines on DR-TB treatment (2018 and 2020 updates), the WHO Global Task Force on the Pharmacokinetics and Pharmacodynamics (PK/PD) of TB medicines and the expert consultation on dosing convened by WHO in October 2021, following the GDG meeting on child and adolescent TB in June 2021. Doses for children and young adolescents weighing <46 kg were revised according to Annex 6 of the 2022 WHO operational handbook on tuberculosis – Module 5: Management of tuberculosis in children and adolescents (153), which was informed by an expert consultation on dosing convened by WHO in October 2021 (154). They are based on the most recent reviews and best practices in the treatment of (paediatric) MDR/RR-TB. For certain medicines the dosages were informed by pharmacokinetic modelling results based on the principle of allometric scaling and maturation (155). Due to the pharmacokinetic properties of certain medicines the doses proposed may exceed the mg/kg/day ranges shown here in order to achieve blood concentrations similar to target levels in an average adult patient. The guidance for the 3–<5 kg weight band and for bedaquiline and delamanid is based on currently available data and may be revised when new data become available.
b Dissolving of crushed adult tablets or capsule content in 10 mL of water is required for administering this dose. The number of mL in the table reflects the dose to provide. This avoids fractioning solid formulations, although bioavailability of the dissolved, crushed adult tablets is uncertain (use of dispersible tablets is preferred).
c The higher dose may be used except when there is risk of toxicity; levels are expected to be lowered because of pharmacokinetic interactions, malabsorption or other reasons; or the strain has low-level drug resistance.
d Bedaquiline adult tablets (100 mg) crushed and suspended in water have been shown to be bioequivalent to tablets swallowed whole. Vigorous stirring/shaking is needed prior to administering the 100 mg tablet crushed and suspended in water.
e When using the 600 mg tab and the 150 mg dt to dose children weighing 16 to <24 kg, the dose in mg/kg will exceed 10–12 mg/kg and clinicians may opt to administer 1.5 dt or 4 mL of the 600 mg tab dispersed in 10 mL water.
f Clofazimine tablets are technically not dispersible but they do dissolve slowly (this takes approximately 5 minutes) in water (5 mL and 10 mL for the 50 mg and 100 mg tablets, respectively). The suspension should be stirred prior to administration. The 50 mg and 100 mg soft gel capsules are difficult to swallow for young children and therefore countries are strongly encouraged to make the 50 mg tablet formulation available.
g In children weighing 3 to <7 kg doses are lower than previously recommended. This is because of relatively high exposures associated with risk of neuropsychiatric adverse events, which is especially concerning when co-administering cycloserine with delamanid.
h Delamanid adult tablets (50 mg) crushed and suspended in water have been shown to be bioequivalent to tablets swallowed whole.
i Amikacin and streptomycin may be used in adults aged 18 years or more, in situations where an effective regimen cannot otherwise be designed using oral agents, when susceptibility is demonstrated and when adequate measures are in place to monitor for adverse events. Given the profound impact that hearing loss can have on the acquisition of language and the ability to learn at school, the use of injectable agents in children should be exceptional and limited to salvage therapy, and the treatment needs to be provided under strict monitoring to ensure early detection of ototoxicity. If used, the weight-based daily dose for amikacin is 15–20 mg/kg and for streptomycin it is 20–40 mg/kg for children aged 2 years and older. To determine the dosing for infants and children aged below 2 years, a paediatric DR-TB expert should be consulted and a lower mg/kg dose used to compensate for immature clearance. Co-administration with lidocaine is advised to reduce pain at the injection site (156).
j These medicines are only recommended as a companion agent (amoxicillin/clavulanic acid) or are not included in Groups A, B and C, because of a lack of data from the latest analysis on longer MDR-TB regimens in adults (isoniazid).
Specific comments on dosing children with medicines used in second-line MDR-TB regimens:
• For dosing of premature and low birth weight infants weighing <3 kg, advice should be sought from a paediatric DR-TB expert.
• For dosing of infants weighing 3 to <5 kg, a paediatric DR-TB expert should be consulted whenever possible.
• The use of child-friendly, dispersible tablets in infants and young children is preferred over manipulating adult tablets or administering or manipulating capsules. Where applicable, the dosing provided is based on dissolving the dispersible formulation in 10 mL of water and administering the number of mL (aliquots). The number of mL in the table reflects the dose to provide. The dissolved solution should be used immediately and the remainder of the 10 mL should be discarded.
• For some weight bands, dosing is indicated with both child-friendly, dispersible formulations and adult formulations. If adult formulations are used, the table provides the dose using aliquots in mL and tablet fractions where applicable (if the fraction is 0.5 or more). Aliquots refer to the volume to administer after crushing and dissolving the tablet in 10 mL of water.

 Обратная связь
Обратная связь