Перекрёстные ссылки книги для ПЛАТФОРМА ВОЗ ПО ОБМЕНУ ЗНАНИЯМИ О ТБ
Tuberculosis (TB) is a leading cause of ill health and mortality from an infectious disease. In 2023, an estimated 10.8 million people fell ill with TB, among whom 1.25 million died from TB (1). TB incidence is closely related to broader socioeconomic determinants such as poverty and food insecurity (1), and undernutrition is one of the most important risk factors that drive the TB epidemic. A systematic review and meta-analysis estimated a 48% prevalence of undernutrition in people with TB (2). People with undernutrition have a more than twofold increased risk of TB (hazard ratio 2.23; 95% confidence interval [CI]: 1.83–2.72) (3), and often have more severe disease, delayed sputum culture conversion, and an elevated risk of death and loss to follow-up (4, 5). TB also commonly causes undernutrition, due to TB-related changes in macronutrient and micronutrient status (6). Thus, the management of TB and undernutrition requires careful attention to achieve adequate nutritional status and to optimize TB treatment outcomes. In addition, nutrition plays a critical role in TB prevention (7). The relationship between undernutrition and TB, including potential points of intervention, is shown in Fig. 1.
Addressing comorbidities and the determinants of TB is a crucial component of World Health Organization’s (WHO’s) End TB Strategy (8), which focuses on integrated people-centred TB care and prevention, including action on TB and comorbidities such as undernutrition. In September 2023, the political declaration of the United Nations (UN) high-level meeting on the fight against TB (9) reaffirmed the commitment to ending the TB epidemic globally by 2030. In the declaration, Member States committed to strengthening comprehensive care and integrating within primary health care the systematic screening, prevention, treatment and care of TB and of related health conditions such as undernutrition.
Fig. 1. Relationship between undernutrition and TB and points of intervention
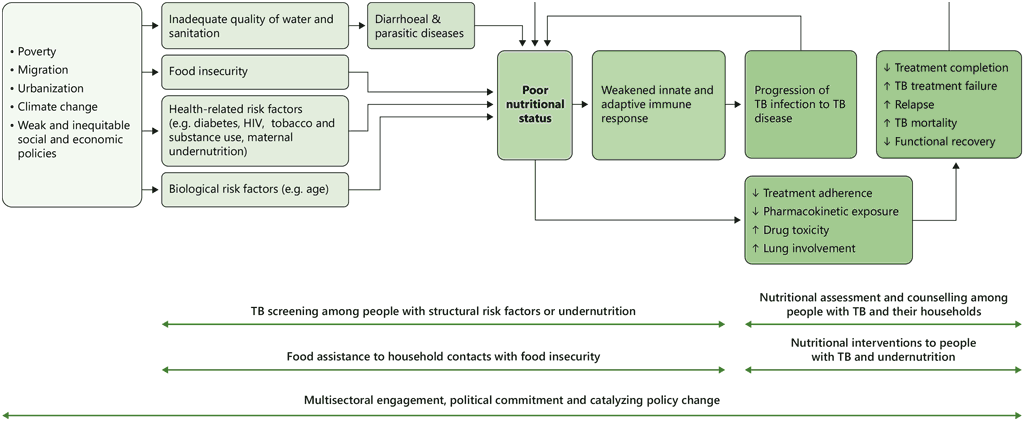
TB: tuberculosis.
Adapted from Sinha et al. 2021 (10).

 Обратная связь
Обратная связь