Liens transversaux de livre pour PLATEFORME DE PARTAGE DES CONNAISSANCES SUR LA TUBERCULOSE DE L'OMS
Sources of information
These information sheets on drugs for the treatment of tuberculosis (TB) represent an update of the sheets first published in the World Health Organization (WHO) document, Companion handbook to the WHO guidelines for the programmatic management of drug-resistant tuberculosis (1), which was based on an adaptation of the publication Drug resistant tuberculosis: a survival guide for clinicians (2). The information has been updated and expanded through a review of multiple sources, including available information on new drugs, recent trials, pharmacokinetics, pharmacodynamics and safety studies. Formulations and dosages have been updated and are in line with the Annex 4 of the WHO operational handbook on tuberculosis. Module 4: Treatment –tuberculosis treatment and care, 2024 update. These formulations are available in quality-assured forms, and have been approved by Stringent Regulatory Authorities, prequalified by WHO or approved by the Expert Review Panel of the Global Fund to Fight AIDS, Tuberculosis and Malaria (Global Fund). WHO recommends using formulations that have been quality assured based on international standards.
Information on drug interactions was sourced primarily from online resources from the United States Food and Drug Administration and the European Medicines Agency.
Bedaquiline (B or Bdq)
ATP: adenosine triphosphate; BMI: body mass index; BPaL: bedaquiline, pretomanid and linezolid; BPaLM: bedaquiline, pretomanid, linezolid and moxifloxacin; CSF: cerebrospinal fluid; ECG: electrocardiograph; HIV: human immunodeficiency virus; M. tuberculosis: Mycobacterium tuberculosis; PI: protease inhibitor; TB: tuberculosis; TdP: torsade de pointes.
a See the handbook Annex 4 for weight bands.
b Upton CM, Steele CI, Maartens G, Diacon AH, Wiesner L, Dooley KE. Pharmacokinetics of bedaquiline in cerebrospinal fluid (CSF) in patients with pulmonary tuberculosis (TB). J Antimicrob Chemother. 2022;77:1720–4. doi: https://doi.org/10.1093/jac/dkac067.
c Court R, Gausi K, Mkhize B, Wiesner L, Waitt C, McIlleron H et al. Bedaquiline exposure in pregnancy and breastfeeding in women with rifampicin-resistant tuberculosis. Brit J Clin Pharm. 2022;88:3548–58. doi: https://doi.org/10.1111/bcp.15380.
d Sirturo (bedaquiline) label. Maryland: United States Food and Drug Administration; 2012 (https://www.accessdata.fda.gov/drugsatfda_docs/label/2012/204384s000lbl.pdf). (See Section 7).
Clofazimine (C or Cfz)
ATP: adenosine triphosphate; CNS: central nervous system; CSF: cerebrospinal fluid; ECG: electrocardiography; M. tuberculosis: Mycobacterium tuberculosis; TB: tuberculosis.
a See the handbook Annex 4 for revised weight-based dosing.
Cycloserine (Cs) or terizidone (Trd)
CNS: central nervous system; CSF: cerebrospinal fluid; M. tuberculosis: Mycobacterium tuberculosis.
a See the handbook Annex 4 for revised weight-based dosing.
Delamanid (Dlm)
BMI: body mass index; CSF: cerebrospinal fluid; ECG: electrocardiography; HIV: human immunodeficiency virus; M. tuberculosis: Mycobacterium tuberculosis; PD: pharmacodynamic; PK: pharmacokinetic; TB: tuberculosis; TdP: torsades de pointes.
a See the handbook Annex 4 for revised weight-based dosing.
b Tucker EW, Pieterse L, Zimmerman MD, Udwadia ZF, Peloquin CA, Gler MT et al. Delamanid central nervous system pharmacokinetics in tuberculous meningitis in rabbits and humans. Antimicrob Agents Chemoth. 2019;63:e00913–19. doi: https://doi.org/10.1128/AAC.00913-19.
Ethambutol (E)
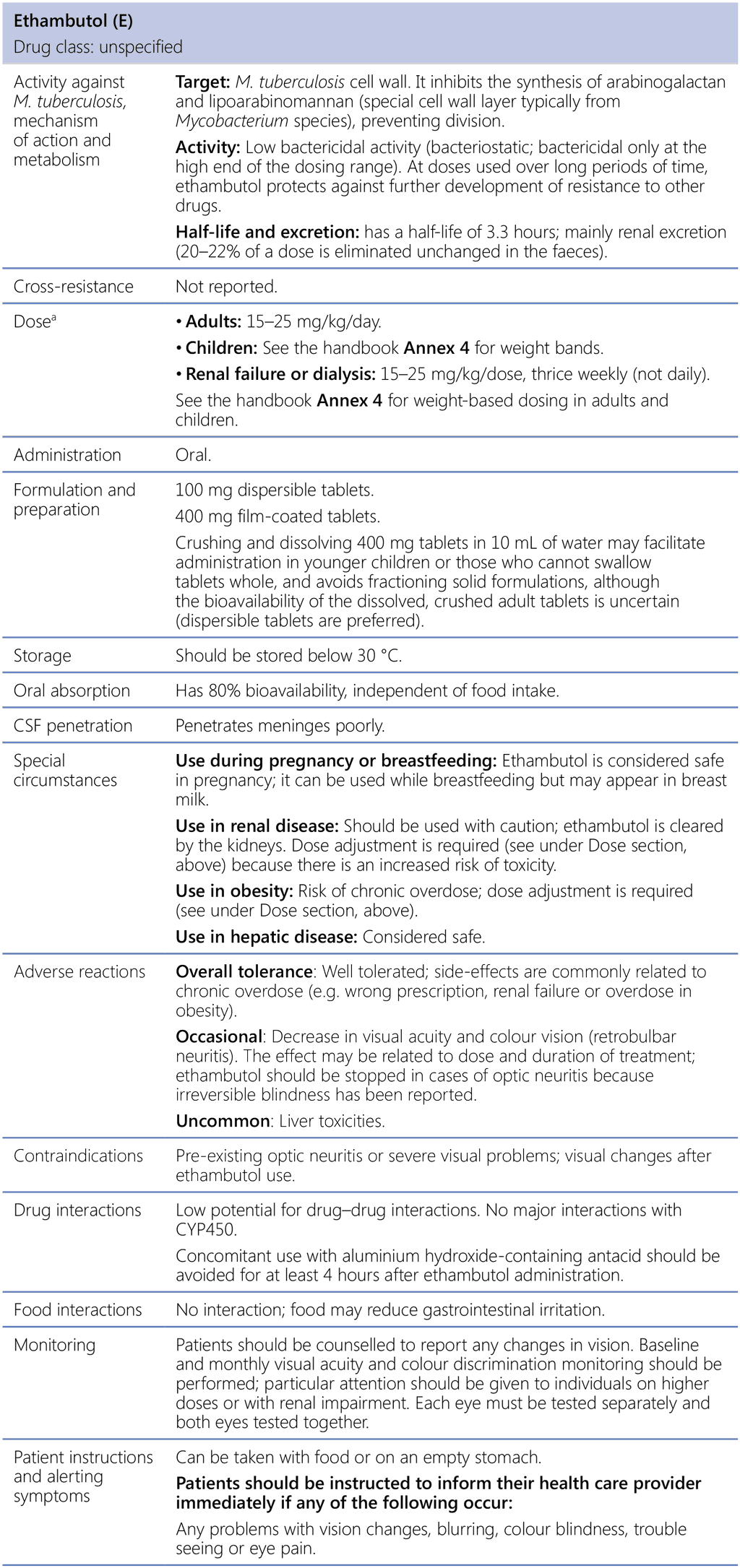
CSF: cerebrospinal fluid; M. tuberculosis: Mycobacterium tuberculosis.
a See the handbook Annex 4 for revised weight-based dosing.
Ethionamide (Eto) or prothionamide (Pto)
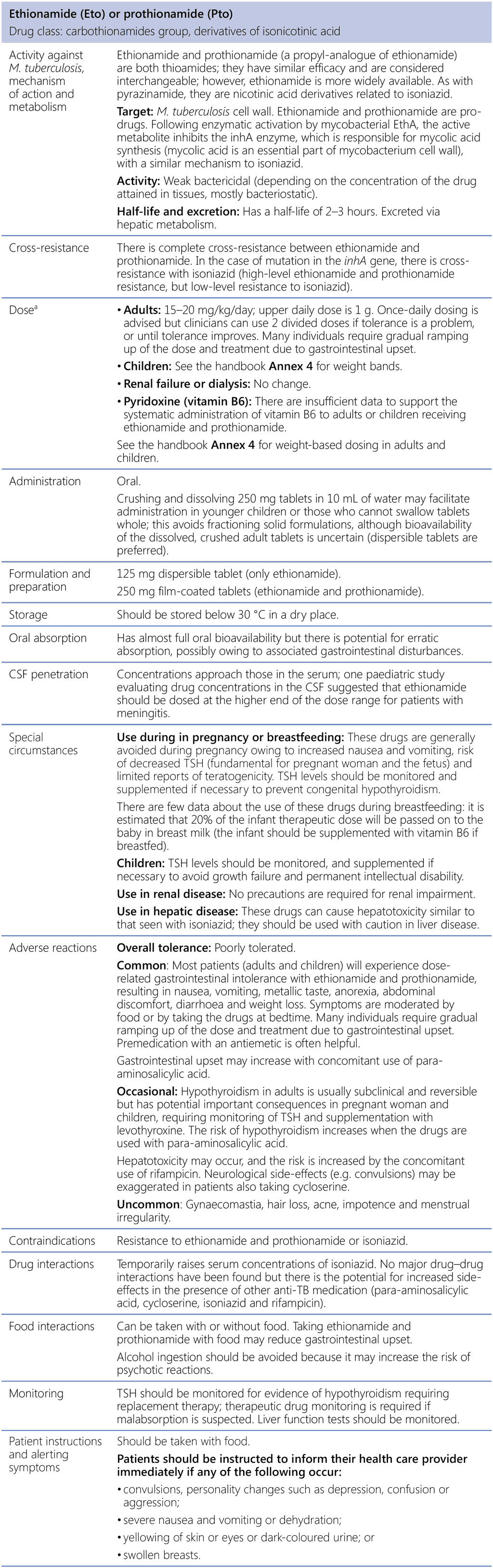
CSF: cerebrospinal fluid; M. tuberculosis: Mycobacterium tuberculosis; TB: tuberculosis; TSH: thyroid-stimulating hormone.
a See the handbook Annex 4 for revised weight-based dosing.
Imipenem–cilastatin (Imp–Cln)
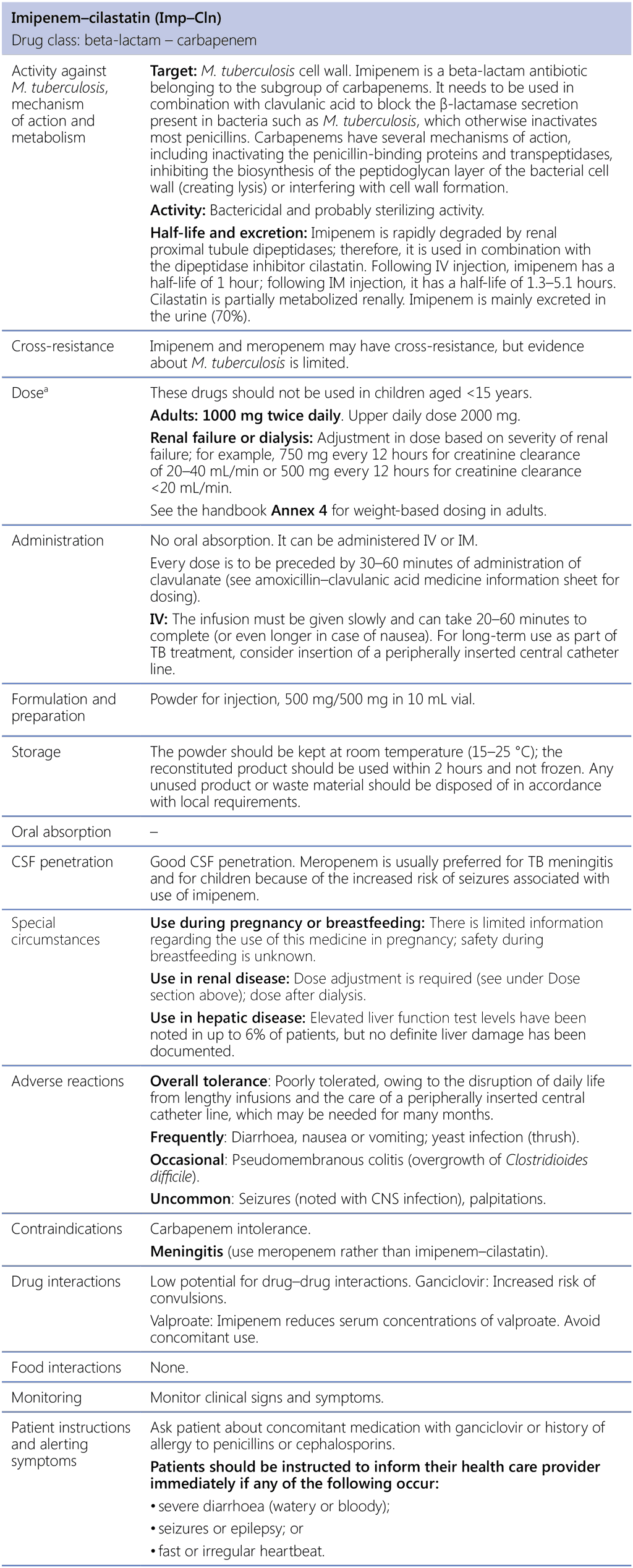
CNS: central nervous system; CSF: cerebrospinal fluid; IM: intramuscular; IV: intravenous; M. tuberculosis: Mycobacterium tuberculosis; TB: tuberculosis.
a See the handbook Annex 4 for revised weight-based dosing.
Isoniazid high dose (Hh)
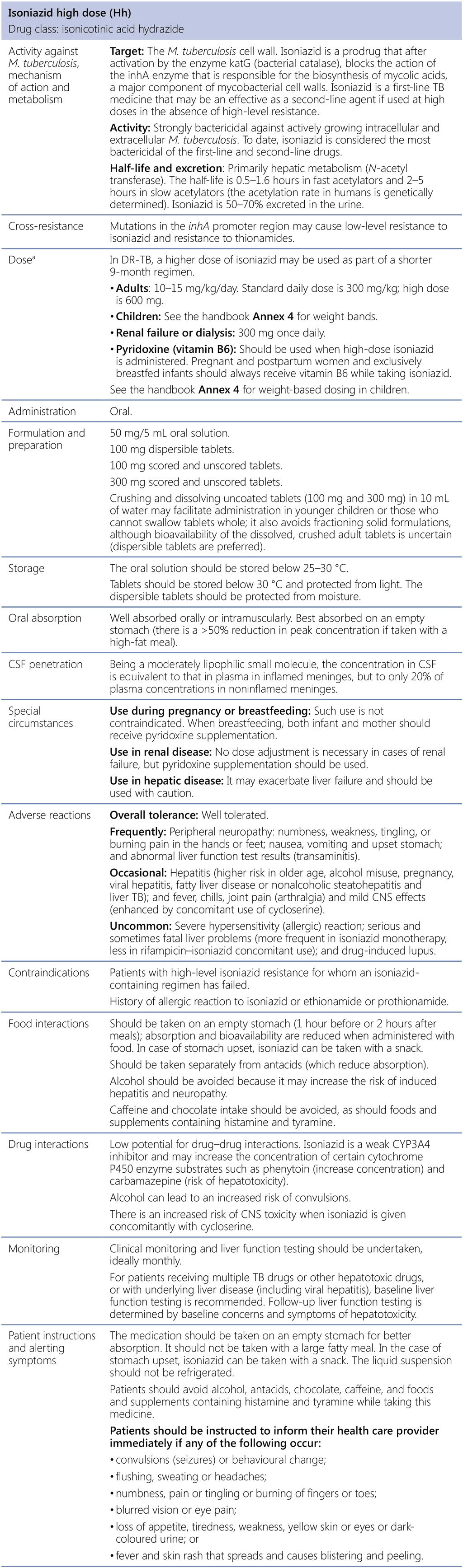
CNS: central nervous system; CSF: cerebrospinal fluid; DR-TB: drug-resistant tuberculosis; M. tuberculosis: Mycobacterium tuberculosis; TB: tuberculosis.
a See the handbook Annex 4 for revised weight-based dosing.
Levofloxacin (Lfx)
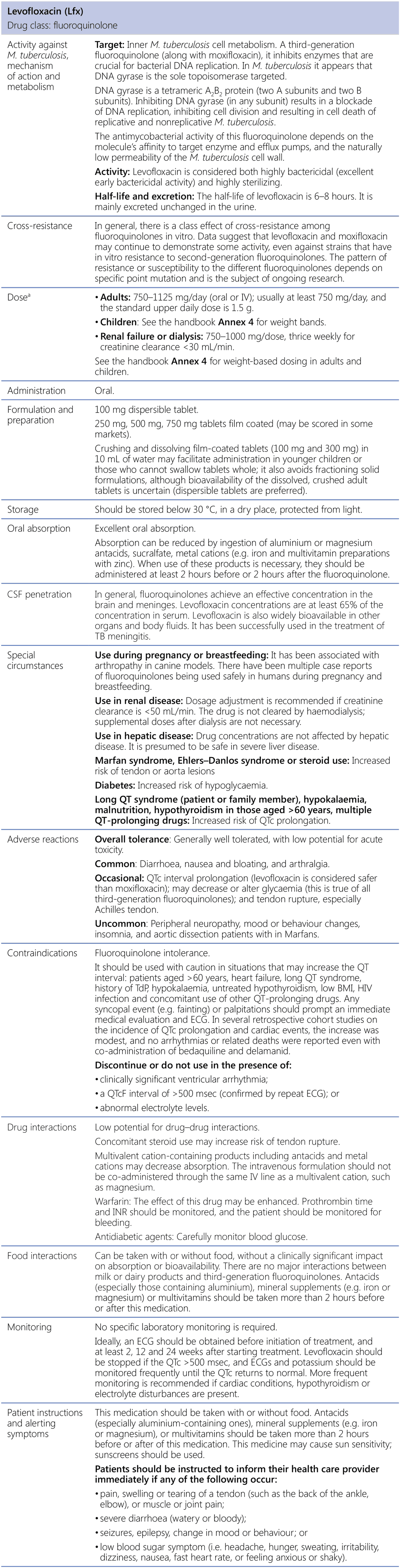
BMI: body mass index; CSF: cerebrospinal fluid; DNA: deoxyribonucleic acid; ECG: electrocardiography; HIV: human immunodeficiency virus; INR: international normalized ratio; IV: intravenous; M. tuberculosis: Mycobacterium tuberculosis; TB: tuberculosis; TdP: torsade de pointes.
a See the handbook Annex 4 for revised weight-based dosing.
Linezolid (L or Lzd)
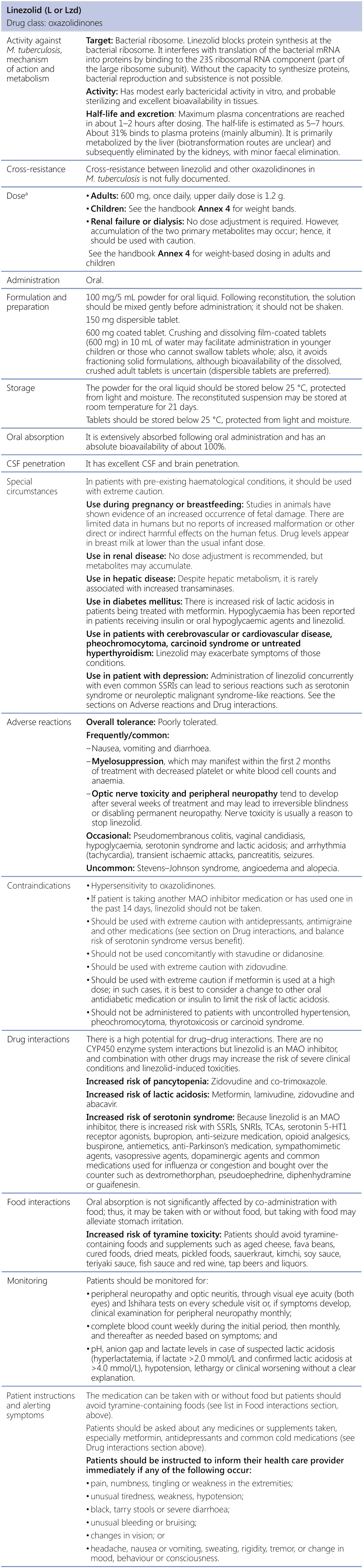
CSF: cerebrospinal fluid; M. tuberculosis: Mycobacterium tuberculosis; MAO: monoamine oxidase; mRNA: messenger ribonucleic acid; RNA: ribonucleic acid; SNRI: serotonin and norepinephrine reuptake inhibitor; SSRI: selective serotonin reuptake inhibitor; TCA: tricyclic antidepressant.
a See the handbook Annex 4 for revised weight-based dosing.
Meropenem (Mpm)
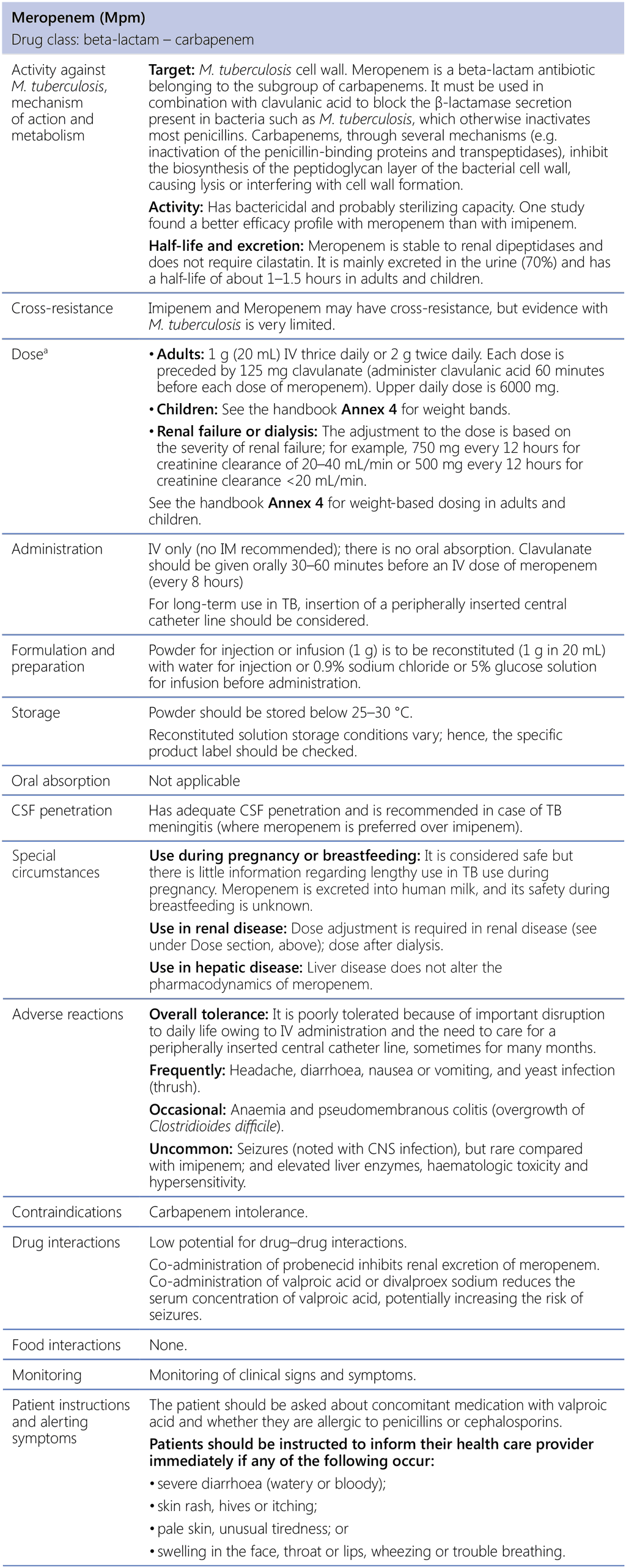
CNS: central nervous system; CSF: cerebrospinal fluid; IM: intramuscular; IV: intravenous; M. tuberculosis: Mycobacterium tuberculosis; TB: tuberculosis.
a See the handbook Annex 4 for revised weight-based dosing.
Moxifloxacin (M or Mfx)
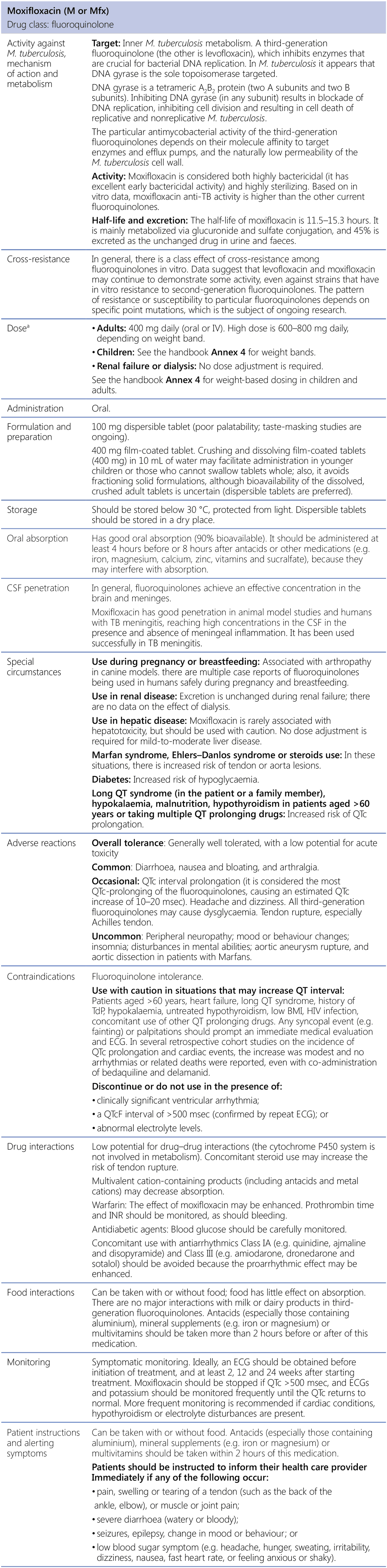
BMI: body mass index; CSF: cerebrospinal fluid; DNA: deoxyribonucleic acid; ECG: electrocardiography; HIV: human immunodeficiency virus; INR: international normalized ratio; IV: intravenous; M. tuberculosis: Mycobacterium tuberculosis; TB: tuberculosis; TdP: torsade de pointes.
a See the handbook Annex 4 for revised weight-based dosing.
Para-aminosalicylic acid (PAS)
CSF: cerebrospinal fluid; M. tuberculosis: Mycobacterium tuberculosis; TSH: thyroid stimulating hormone.
a See the handbook Annex 4 for revised weight-based dosing.
Pretomanid (Pa)
1 Howell, Pauline. Results of studies on pretomanid: side effects on male fertility and PK/PD in female children. Presented during: WHO BPaLM Accelerator Virtual Meeting on 28 May 2024.
AUC: area under the curve; BPaL: bedaquiline, pretomanid and linezolid; BPaLM: bedaquiline, pretomanid, linezolid and moxifloxacin; CSF: cerebrospinal fluid; Ddn: deazaflavin-dependent nitroreductase; ECG: electrocardiography; GGT: gamma-glutamyl transferase; HIV: human immunodeficiency virus; M. tuberculosis: Mycobacterium tuberculosis; TB: tuberculosis; WHO: World Health Organization.
a See the handbook Annex 4 for revised weight-based dosing.
Pyrazinamide (Z)
ALT: alanine transaminase; AST: aspartate transaminase; CSF: cerebrospinal fluid; M. tuberculosis: Mycobacterium tuberculosis; TB: tuberculosis; ULN: upper limit of normal.
a See the handbook Annex 4 for revised weight-based dosing.
Rifampicin (R)
Rifapentine
Amikacin (Am)
CSF: cerebrospinal fluid; D5W: dextrose 5% in water; IM: intramuscular; IV: intravenous; M. tuberculosis: Mycobacterium tuberculosis; TB: tuberculosis; t-RNA: transfer ribonucleic acid; WHO: World Health Organization.
a See the handbook Annex 4 for revised weight-based dosing.
Streptomycin (Sm)
BMI: body mass index; CSF: cerebrospinal fluid; IM: intramuscular; IV: intravenous; M. tuberculosis: Mycobacterium tuberculosis; WHO: World Health Organization.
a See the handbook Annex 4 for revised weight-based dosing.
References (Annex 1)
- Companion handbook to the WHO guidelines for the programmatic management of drug-resistant tuberculosis. Geneva: World Health Organization; 2014 (https://apps.who.int/iris/handle/10665/130918).
- Curry International Tuberculosis Center, California Department of Public Health. Drug-resistant tuberculosis: a survival guide for clinicians. California: University of California San Francisco; 2016 (https://www.currytbcenter.ucsf.edu/products/view/drug-resistant-tuberculosis-survival-guide-clinicians-3rd-edition).
- WHO-PQ recommended summary of product characteristics. Geneva: Wold Health Organization; 2022 (https://extranet.who.int/prequal/sites/default/files/whopar_files/TB388part4v1.pdf).
- Cerrone M, Bracchi M, Wasserman S, Pozniak A, Meintjes G, Cohen K et al. Safety implications of combined antiretroviral and anti-tuberculosis drugs. Expert Opin Drug Saf. 2020;19:23–41 (10.1080/14740338.2020.1694901).
- Tyeku N, Apolisi I, Daniels J, Beko B, Memani B, Cengani L et al. Pediatric delamanid treatment for children with rifampicin-resistant TB. Int J Tuberc Lung Dis. 2022;26:986–8 (10.5588/ijtld.22.0264).
- Summary and recommendations from the second joint meeting of the WHO Global Advisory Committee on Vaccine Safety (GACVS) and Advisory Committee on Safety of Medicinal Products (ACSoMP) 14–16 december 2022. Geneva: 2022 (https://www.who.int/publications/m/item/2022-december-acsomp-recommendations).
- Burke A, Alffenaar J, Denholm J. Evidence of safety for pretomanid and male reproductive health. Int J Tuberc Lung Dis. 2022;26:473–4 (10.5588/ijtld.22.0092).
- Boekelheide K, Olugbosi M, Nedelman J, Everitt D, Smith E, Betteridge M et al. Male reproductive hormones in patients treated with pretomanid. Int J Tuberc Lung Dis. 2022;26:558–65 (10.5588/ijtld.21.0654).
- Global Alliance for TB Drug Development. A Trial to Evaluate the Male Reproductive Safety of Pretomanid in Adult Male Participants With Drug Resistant Pulmonary Tuberculosis (PaSEM). 2025 (https://clinicaltrials.gov/study/NCT04179500).

 Retour
Retour